Response of five shallot varieties applied with Bacillus spp. against twisted disease
Main Article Content
Abstract
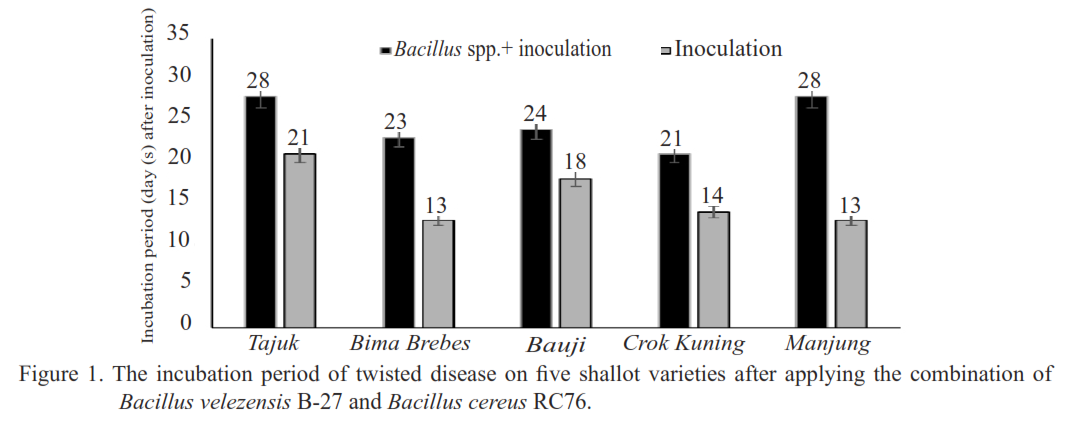
The use of several shallot varieties applied with the biological agent Bacillus spp. is one of the most developed methods of controlling twisted disease, as it is safe and efficient. The large number of shallot varieties released to farmers requires the selection of varieties with the best resistance response to twisted disease. This study aimed to determine the different responses between five local shallot varieties treated with a combination of Bacillus velezensis B-27 and B. cereus RC76 against the twisted disease. This study was conducted in a greenhouse and on the field using Tajuk, Bima Brebes, Bauji, Crok Kuning, and Manjung varieties, which were dipped and sprayed with a B. velezensis B-27 and B. cereus RC76. The treatment of B. velezensis B-27 and B. cereus RC76 on five varieties showed a good response to suppressing twisted disease. The twisted disease incubation period in five varieties treated with the combination of B. velezensis B-27 and B. cereus RC76 showed a slower result than the control, the disease incidence and intensity could be reduced by 70 90%. The best resistance response of varieties treated with the combination of B. velezensis B-27 and B. cereus RC76 was shown by Tajuk compared to the other four varieties.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
Aprilia I, Maharijaya A, & Wiyono, S. 2020. Keragaman genetik dan ketahanan terhadap penyakit layu Fusarium (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp cepae) bawang merah (Allium cepa L. var. aggregatum) Indonesia [Genetic diversity and Fusarium wilt disease resistance (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cepae) of Indonesian shallots (Allium cepa L. var aggregatum). Jurnal Hortikultura Indonesia. 11(1): 32–40. https://doi.org/10.29244/jhi.11.1.32-40
Cahyaningrum H, Suryanti, & Widiastuti A. 2020. Response and resistance mechanism of shallot var. Topo, a North Molluca’s local variety against basal rot disease. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Food, Agriculture and Natural Resources (FANRes 2019). pp. 71–75. https://doi.org/10.2991/aer.k.200325.015
Chen Q, Qiu Y, Yuan Y, Wang K, & Wang H. 2022. Biocontrol activity and action mechanism of Bacillus velezensis strain SDTB038 against Fusarium crown and root rot of tomato. Front. Microbiol. 13: 994716. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.994716
Djaenuddin N, Muis A, & Nonci N. 2018. Screenhouse test of eight biopesticide formulation Bacillus subtilis against downy mildew, Peronosclerospora philipinensis, on corn plant. J. Trop. Plant Pests Dis. 18(1): 51–56. https://doi.org/10.23960/j.hptt.11851-56
Emeliawati, Salamiah, & Fitriyanti D. 2022. Pengendalian penyakit moler (Fusarium oxysporum) pada bawang merah dengan serbuk kulit jengkol (Pithecellobium jiringa) di lahan gambut [Control of twisted disease (Fusarium oxysporum) on shallots with jengkol bark powder (Pithecellobium jiringa) in peatlands]. Proteksi Tanaman Tropika. 5(2): 499–505. https://doi.org/10.20527/jptt.v5i2.1255
Hadiwiyono, Sari K, & Poromarto SH. 2020. Yields losses caused by basal plate rot (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cepae) in some shallot varieties. Caraka Tani: Journal of Sustainable Agriculture. 35(2): 250–257. https://doi.org/10.20961/carakatani.v35i2.26916
Herlina L, Istiaji B, & Wiyono S. 2021. The causal agent of Fusarium disease infested shallots in Java Islands of Indonesia. E3S Web of Conferences. 232: 03003. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202123203003
Ilmiah HH, Sulistyaningsih E, & Joko T. 2021. Fruit morphology, antioxidant activity, total phenolic and flavonoid contents of Salacca zalacca (Gaertner) Voss by applications of goat manures and Bacillus velezensis B-27. Caraka Tani: Journal of Sustainable Agriculture. 36(2): 270–282. https://doi.org/10.20961/carakatani.v36i2.43798
Jeger MJ & Viljanen-Rollinson SLH. 2001. The use of the area under the disease-progress curve (AUDPC) to assess quantitative disease resistance in crop cultivars. Theor. Appl. Genet. 102(1): 32–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051615
Khan N, Maymon M, & Hirsch AM. 2017. Combating Fusarium infection using Bacillus-based antimicrobials. Microorganisms. 5(4): 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms5040075
Le D, Audenaert K, & Haesaert G. 2021. Fusarium basal rot: profile of an increasingly important disease in Allium spp. Trop. Plant Pathol. 46: 241–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-021-00421-9
Lestiyani A, Wibowo A, & Subandiyah S. 2021. Pathogenicity and detection of phytohormone (gibberellic acid and indole acetic acid) produced by Fusarium spp. that causes twisted disease in shallot. Jurnal ProteksiTanaman. 5(1): 24–33. https://doi.org/10.25077/jpt.5.1.24-33.2021
Maharijaya A, Harti H, Nuryana FI, Rosyidin C, Suryo, Helmi, Sulistyono A, & Akat. 2016. Description of Tajuk Shallot Variety. Agriculture Department of Nganjuk District. https://hortikultura.pertanian.go.id/. Accessed 20 February 2023.
Nifakos K, Tsalgatidou PC, Thomloudi EE, Skagia A, Kotopoulis D, Baira E, Delis C, Papadimitriou K, Markellou E, Venieraki A, & Katinakis P. 2021. Genomic analysis and secondary metabolites production of the endophytic Bacillus velezensis Bvel1: A biocontrol agent against Botrytis cinerea causing bunch rot in post-harvest table grapes. Plants. 10(8): 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081716
Ntushelo K, Ledwaba LK, Rauwane ME, Adebo OA, & Njobeh PB. 2019. The mode of action of Bacillus species against Fusarium graminearum, tools for investigation, and future prospects. Toxins. 11(10): 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100606
Prakoso EB, Wiyatingsih S, & Nirwanto H. 2016. Uji ketahanan beberapa kultivar bawang merah (Allium ascalonicum) terhadap infeksi penyakit moler (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cepae) [Endurance test on different cultivars shallots (Allium ascalonicum) against infectious diseases moler (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cepae)]. Plumula. 5(1): 10–20.
Pusat Data dan Sistem Informasi Pertanian (Pusdatin). 2013. Workshop Hasil Pengembangan Metode Konversi Bawang Merah [Workshop of Convertion Method Development Result of Shallot]. Kementrian Pertanian. Jakarta.
Rabbee MF, Ali MDS, Choi J, Hwang BS, Jeong SC, & Baek KH. 2019. Bacillus velezensis: A valuable member of bioactive molecules within plant microbiomes. Molecules. 24(6): 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061046
Rahma AA, Suryanti, Somowiyarjo S, & Joko T. 2020. Induced disease resistance and promotion of shallot growth by Bacillus velezensis B-27. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 23(9): 1113–1121. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2020.1113.1121
Ramírez V, Martínez J, Bustillos-Cristales MDR, Catañeda-Antonio D, Munive JA, & Baez A. 2022. Bacillus cereus MH778713 elicits tomato plant protection against Fusarium oxysporum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 132(1): 470–482. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15179
Rohma M & Wahyuni WS. 2022. Pengendalian penyakit layu Fusarium oxysporum f.sp cepae pada tanaman bawang merah dengan air rebusan serai dapur (Cymbopogon citratus) [Control of wilt disease (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cepae) on shallots with lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) boiled water. Berkala Ilmiah Pertanian. 5(2): 65–69. https://doi.org/10.19184/bip.v5i2.28856
Simko I & Piepho HP. 2012. The area under the disease progress stairs: Calculation, advantage, and application. Phytopathology. 102(4): 348-451. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-07-11-0216
Sudana M & Lotrini M. 2005. Pengendalian terpadu penyakit layu (Ralstonia solanacearum Smith) dan nematoda puru akar (Meloidogyne spp.) pada tanaman jahe gajah. J Trop Plant Pests Dis. 5(2): 97–103. https://doi.org/10.23960/j.hptt.2597-103
Wang C, Zhao D, Qi G, Mao Z, Hu X, Du B, Liu K, & Ding Y. 2020. Effects of Bacillus velezensis FKM10 for promoting the growth of Malus hupehensis Rehd. and inhibiting Fusarium verticillioides. Front. Microbiol. 10: 2889. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02889
Wibowo A, Kaeni E, Toekidjo T, Subandiyah S, Sulistyaningsih E, & Harper S. 2016. Responses of four shallot (Allium cepa L. Aggregatum Group) cultivars to moler disease (Fusarium spp.) after bulb treatment. Acta Hortic. 1143: 69–76. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2016.1143.11
Wijoyo RB, Sulistyaningsih E, & Wibowo A. 2020. Growth, yield and resistance responses of three cultivars on true seed shallots to twisted disease with salicylic acid application. Caraka Tani: Journal of Sustainable Agriculture. 35(1): 1–11. https://doi.org/10.20961/carakatani.v35i1.30174
Wiyatiningsih S. 2021. A study on twisting disease epidemic on shallot. AcademiaLetters. 1516. https://doi.org/10.20935/al1516
Wiyatiningsih S, Wibowo A, & Triwahyu E. 2009. Tanggapan tujuh kultivar bawang merah terhadap infeksi Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cepae penyebab penyakit moler [Responses of seven shallot cultivars to infection of Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cepae cause of moler disease. Jurnal Pertanian MAPETA. 12(1): 7–13.
Wulan EIR, Wibowo A, Joko T, & Widiastuti A. 2022. Induced resistance mechanism of twisted disease suppression of shallot by Bacillus spp. Jurnal Perlindungan Tanaman Indonesia. 26(1): 40–50. https://doi.org/10.22146/jpti.73198
Ye M, Tang X, Yang R, Zhang H, Li F, Tao F, Li F, & Wang Z. 2018. Characteristics and application of a novel species of Bacillus: Bacillus velezensis. ACS Chem. Biol. 13(3): 500–505. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00874
Zhou H, Ren ZH, Zu X, Yu XY, Zhu HJ, Li XJ, Zhong J, & Liu EM. 2021. Efficacy of plant growth-promoting bacteria Bacillus cereus YN917 for biocontrol of rice blast. Front. Microbiol. 12: 684888. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.684888